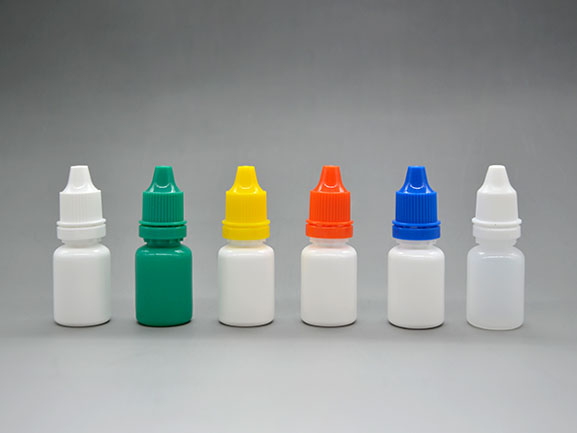
If you're developing an ophthalmic solution, you know that the formulation is everything. But did you know that the eye drop bottle material is just as critical to your product's success? The wrong choice can lead to stability issues, drug absorption, and even patient harm.
As a trusted eye drop bottle manufacturer, we help pharmaceutical companies navigate this crucial decision every day. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the most common materials used, their properties, and how to choose the right one for your specific application.
Why the "Container" is a Critical Component
The eye is exceptionally sensitive. The plastic bottle housing your solution must be:
Inert: It cannot interact with or absorb the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Sterilizable: It must withstand sterilization processes like gamma irradiation or ETO without degrading.
Durable: It must protect the solution from external contaminants and environmental factors.
Squeezable: It must allow for easy, controlled dosing by the patient.
The material you select directly impacts all these factors. Let's compare the two most common contenders.
LDPE vs. HDPE: The Head-to-Head Comparison
Most eye drop bottles are made from polyolefins, with Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) being the industry standards.
| Feature | Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
| Flexibility | High (Soft, squeezable) | Low (Semi-rigid, harder to squeeze) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (But can be permeable to some gases/vapors) | Excellent (Superior barrier properties) |
| Clarity | Translucent | Opaque or Translucent |
| Impact Strength | High (Less prone to cracking) | High |
| Common Use | Standard multi-dose eye drops | Preservative-free systems, sensitive formulations |
Deep Dive into the Materials
1. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE is the most common material for eye drop bottles, and for good reason.
Pros: Its high flexibility makes it incredibly user-friendly. Patients with reduced hand strength, such as the elderly or those with arthritis, find LDPE bottles easy to squeeze for a consistent drop. It offers good chemical resistance for a wide range of ophthalmic solutions.
Cons: LDPE has relatively higher gas and vapor permeability compared to HDPE. This means oxygen and carbon dioxide can potentially pass through the container walls over time, which could be a concern for extremely oxygen-sensitive formulations.
Best For: The vast majority of multi-dose eye drops, especially those containing preservatives.
2. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is the strong, robust counterpart to LDPE.
Pros: Its superior barrier properties make it the gold standard for protecting sensitive formulations from external gases and moisture. This is critical for preservative-free multi-dose eye drops that rely on the container itself (often with a special filter) to maintain sterility. It is also more rigid, which can help prevent accidental squeezing during shipping.
Cons: The lower flexibility can make it harder for some patients to administer a drop, potentially affecting compliance.
Best For: Preservative-free formulations, sensitive drugs prone to oxidation, and products requiring an extra-strong moisture barrier.
Beyond LDPE and HDPE: Other Material Considerations
While LDPE and HDPE cover 95% of the market, other options exist for specialized applications:
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): Used for some single-dose, preservative-free systems. PET offers excellent clarity and barrier properties but is not squeezable in the same way—it’s often used in blow-fill-seal technology.
PP (Polypropylene): Often used for the bottle cap and dropper tip due to its high rigidity and chemical resistance.
5 Key Factors for Choosing Your Eye Drop Bottle Material
How do you make the final decision? Ask these critical questions:
What is the Sensitivity of Your Formulation? Is it prone to oxidation or moisture degradation? If yes, HDPE is likely your best bet.
Is Your Product Preservative-Free? For multi-dose preservative-free systems, the superior barrier of HDPE is almost always required to work in tandem with the filtration system.
Who is Your Target Patient? For a geriatric market, the easy squeezability of LDPE can greatly improve user experience and compliance.
What is Your Sterilization Method? Both LDPE and HDPE tolerate gamma and ETO sterilization well, but it's crucial to validate this with your manufacturer.
What are Your Clarity Needs? If seeing the solution level is a key user requirement, translucent LDPE is the preferred choice.
Partner with an Expert in Ophthalmic Packaging
The choice between LDPE and HDPE is not just a technical specification—it's a strategic decision that affects drug stability, patient compliance, and ultimately, the success of your product.
At Xinfuda, we don't just sell bottles; we provide packaging solutions. Our technical experts will work with you to analyze your formulation, target market, and regulatory needs to recommend the perfect eye drop bottle material for your product.
Ready to make the right choice for your ophthalmic solution?